Arthrosis (osteoarthritis) is a degenerative disease of cartilage tissue in which the normal functioning of the joint is disrupted. In most cases, the disease is chronic. Shoulder arthrosis is characterized by pain and gradual loss of hand functionality. Most of the time, the pathology is detected in old age. The causes of osteoarthritis are senile changes in the body, shoulder injuries, birth defects and constant stress on the shoulder girdle. If a person experiences discomfort in the shoulder girdle, it is necessary to see a doctor and get an exam. With the help of a complex effect, it is possible to stop the development of degenerative changes.
What is shoulder arthrosis
Arthrosis of the shoulder - injury to the cartilage tissue of the joint, during which degenerative changes occur. The blood supply is cut off in the cartilage tissue so that it fails to receive enough nutrients and oxygen.At risk are people who suffer daily from excessive stress on their shoulders and have congenital tissue defects in their joints.In the early stages, the person experiences acute pain, but normal shoulder functionality is preserved. If the triggering factors are not eliminated, the disease will cause serious damage to health.
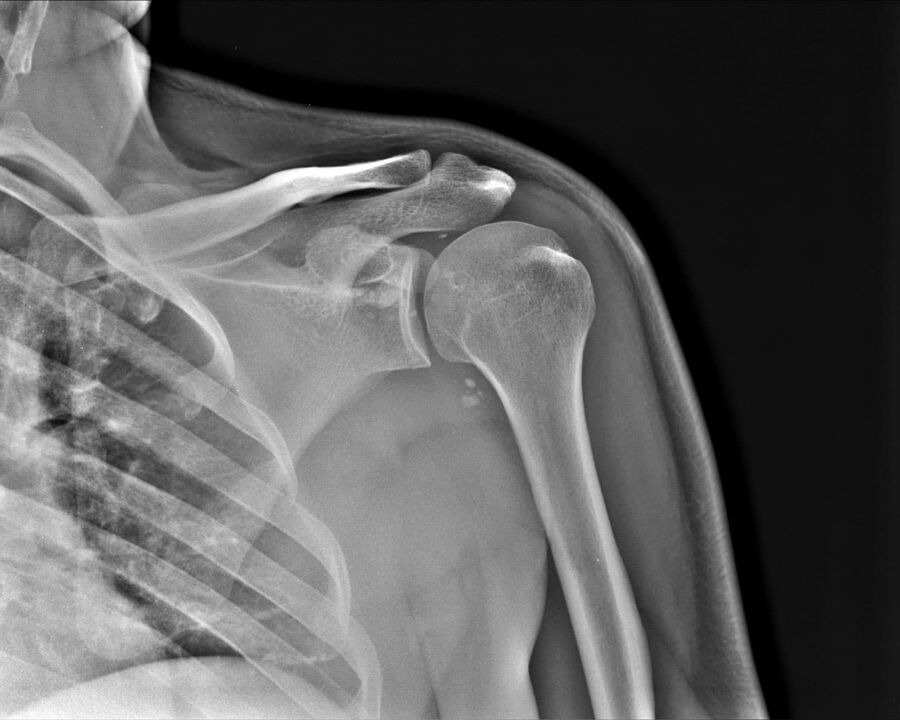
Diagnosis plays an important role in the treatment of arthrosis. With the help of X-rays, it is possible to accurately determine the cause of the disease and the degree of damage.
anatomical background
Congenital disorders of the structure of joints and connective tissue can become the causes of the onset of the disease. If a person has characteristics in the structure of the shoulder girdle, even a common load can cause the onset of arthrosis. To avoid problems, you will need to take preventative measures and regularly visit a doctor. Congenital dysplasia can be managed with massage and exercise therapy.
Causes and risk factors
All elderly people are at risk.According to WHO statistics, the probability of developing arthrosis after 45 years increases significantly.At age 65, more than 50% of people suffer from this disease. Among the reasons that cause the early onset of the disease are:
- shoulder rotator cuff damage;
- shoulder injury;
- constant stress associated with sports or work;
- infectious and autoimmune pathologies;
- obesity;
- improper metabolism.
The older a person gets, the greater the risk of developing degenerative joint damage.
Views
The defeat of cartilaginous tissue is divided into primary and secondary. The diagnosis of primary arthrosis is made if there are no concomitant diseases. It is usually detected in old age. The reason for its appearance is age-related changes. Secondary vision occurs due to injuries or in the context of another illness. Furthermore, the disease is classified by location.Degenerative changes in the shoulder can occur in the shoulder joint area or in the acromioclavicular joint.
Stages of Development and Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the stage of development of the shoulder arthrosis. The pathology is divided into three stages:
- The first. . . There are pains that intensify at night, the functionality of the shoulder girdle is preserved.
- The second. . . When you move your hands, you hear a snap, the pain is constant, there is limited mobility in the shoulder.
- Third. . . Severe pain, arm is fixed in one position, protrusions are visible in the affected area, severe joint deformation is noticeable on x-ray.
The disease may not develop for a long time. If a person continues to carry the shoulder girdle, the situation will get worse.
Which doctor to contact
Arthrosis of the shoulder joint is treated by different doctors. The initial examination is performed by a therapist or rheumatologist. In addition, the following specialists may be involved in the treatment:
- surgeon;
- orthopedist;
- neurologist.
In most cases, the treatment regimen is designed by a rheumatologist.The help of a surgeon is needed if the disease requires surgical treatment or intra-articular manipulations.Consultation with a neurologist is necessary if the nerve bundle has been compressed due to illness.
Only after a diagnostic test will the therapist or rheumatologist determine if help from other specialists is needed.
Diagnosis

Hardware and laboratory tests as well as manual exams are used to make an accurate diagnosis. First, an inspection with multiple tests is carried out. The person's history is being studied. All of this helps to make a preliminary diagnosis. In addition, MRI and X-ray are used to determine the degree of narrowing of the joint space, the condition of blood vessels, synovium, tendons.
manual exam
Manual examination includes palpation of the affected area and performing diagnostic tests. Pain usually occurs on palpation of the acromioclavicular joint. If a person has trouble putting their hand behind their head, this may indicate the presence of arthrosis of the shoulder joint. During a manual examination, your doctor will be able to detect inflammation. Information obtained during the manual examination plays an important role in diagnosis.The examination should be performed by an experienced rheumatologist or therapist so as not to cause harm during functional testing and testing.
instrumental methods
Instrumental research methods allow you to determine:
- the degree of narrowing of the joint space;
- irregular joint surface;
- location of arthrosis.
After using instrumental diagnostic methods, the required therapy is selected. For diagnosis, radiography, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging are used. These methods provide the necessary information. Instrumental examination may be repeated during treatment.
Laboratory
Laboratory tests allow you to assess the condition of the body as a whole, in addition to ruling out inflammatory arthritis. First, blood is collected for analysis. In arthrosis, all indications for clinical and biochemical blood tests are within normal limits. In arthritis, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, the amount of immunoglobulins and other markers of the inflammatory process in the body increase significantly. Based on the results obtained, the physician makes a final diagnosis and selects an effective treatment regimen.
For accurate results, donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach.
Treatment
The treatment approach is complex. Medicines, physiotherapy, physiotherapy exercises are used. If the disease is advanced or does not respond to treatment, surgery is used. Basic principles of therapy:
- relieve pain;
- stop the development of the disease;
- start the mechanisms for restoring the cartilaginous tissue.
In the initial phase, the result is achieved through the use of medication.It is important to exclude provocation factors. Stable remission is achieved through physical therapy and exercise therapy.
medicine
The following groups of drugs can be used for treatment:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory;
- chondroprotectors;
- corticosteroids;
- vasodilators.
NSAIDs and corticosteroids are used to relieve pain. They apply for a limited period of time. Chondroprotectors can accelerate the restoration of cartilage tissue. Vasodilators help improve blood flow and relieve small vessel spasm.
Before prescribing this or that remedy, it is necessary to carefully study the contraindications. Only a doctor can correctly combine all medications.
Surgical
Surgical intervention is only performed as a last resort, when irreversible degenerative processes have occurred. The reasons for the operation are:
- lack of effect of conservative therapy;
- the occurrence of complications;
- the appearance of severe degenerative changes.
If the joint has lost its original appearance, arthroplasty is performed.The diseased joint is replaced by an artificial one. The operation is complex and requires high surgeon qualification. Puncture and arthroscopy can also be performed to treat arthrosis.
Puncture
The puncture is performed if a large amount of fluid accumulates in the joint cavity. In addition, this procedure is performed with infectious inflammations to determine the type of infection. Getting rid of excess fluid helps reduce pressure on the shoulder joint and increase your mobility. The procedure is minimally invasive, so recovery after completion occurs as quickly as possible. The puncture has indications and contraindications. It is used only in case of accumulation of fluid in the joint capsule or suspicion of an infectious complication of arthrosis.
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that removes damaged cartilage from the shoulder. The operation is performed with endoscopic equipment and a microcamera. The advantage of this treatment method is quick rehabilitation. Removing the destroyed cartilage allows you to relieve stress and restore joint mobility. The downside of the procedure is that access to the affected area is somewhat limited.
Endoprosthesis
A stent graft is a complete replacement of a damaged joint with a biocompatible analogue.Titanium construction is commonly used. The operation allows you to get rid of even stage 3 osteoarthritis. Long-term rehabilitation is carried out after the stent graft. With this, it is possible to achieve complete elimination of affected areas and chronic pain, as well as restore mobility to the shoulder girdle.
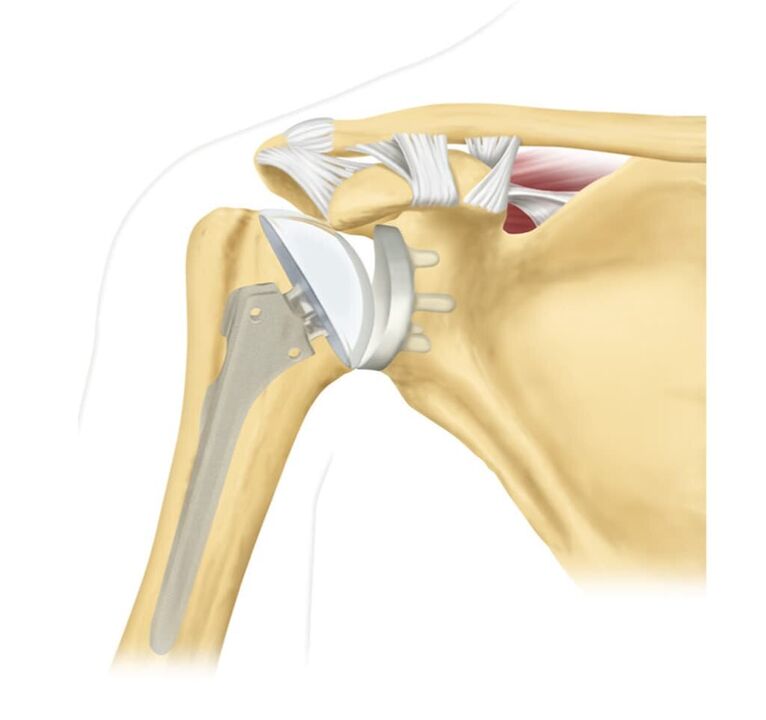
Operation is not always possible. In older people, the rehabilitation period is much more difficult. Other treatment options are used before the arthroplasty appointment.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy procedures play an important role in eliminating arthrosis in the shoulder girdle. With their help, it is possible to restore normal joint mobility and reduce the intensity of pain. The following procedures are performed:
- electrophoresis;
- local cryotherapy;
- magnetotherapy.
Physical therapy can be used if there are no acute manifestations of the disease (severe pain, difficulty in walking). Regular exposure will completely eliminate discomfort. Any procedure must be performed by a qualified technician.Before visiting the physiotherapy rooms, you need to consult your doctor.
Kinesitherapy
Kinesiotherapy refers to the use of active and passive methods to restore shoulder functionality. If the illness is mild, the person can begin using an active method of recovery through exercise. The passive method consists of external exposure through massage or mechanotherapy. Kinesiotherapy helps to quickly eliminate the manifestations of arthrosis in the shoulder joint.
The passive method of recovery through mechanotherapy is available for people of any age.
exercise therapy
Physical therapy exercises allow you to overload your muscles and restore mobility to your shoulder joint. Static exercises are mainly used. A dynamic load in which active shoulder rotation is performed is undesirable. The following exercises can be performed:
- shoulders shaking- it is necessary to assume the starting position, sitting in a chair and placing your hands on your knees. Relax your shoulders and start swinging your elbows. At the same time, your hands are on your knees.
- slow rotation- you need to sit in a chair and put your hands on your knees and then start to rotate your shoulders slowly with short breaks. Circular movements are performed back and forth.
Physical therapy can only be used during remission, when pain and limitation of movement is almost completely absent.
Massage
Massaging the affected area allows you to get the following effects:
- improve tissue nutrition;
- relieve swelling;
- tone your muscles;
- remove the pain.
It is advisable that all actions are carried out by a qualified specialist. When performing self-massage, strong pressure and sudden movements should be avoided.The result of the massage effect is noticeable a few weeks after regular use.
Massage must be accompanied by other activities. If a person performs exercises from the exercise therapy complex and visits a massage room, he will get great results.
Mechanotherapy
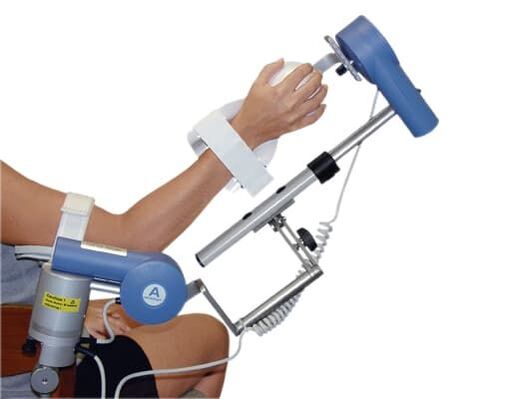
Mechanotherapy is a set of exercises performed by specialized mechanisms. This method allows recovery in the shortest possible time. Mechanotherapy is ideal for rehabilitation after surgery. Special mechanisms allow you to adjust the load, allowing for faster recovery of muscles and ligaments. All actions are performed under stationary conditions. Classes on rehabilitation mechanisms should be taught with an instructor. It will correctly select the required load and simulator.
joint traction
The joints are stretched using a specialized device. With this procedure, the following effects can be achieved:
- improve blood circulation;
- expand the joint space;
- relieve tension in the ligaments.
The narrowing of the joint space is one of the main manifestations of arthrosis. With this procedure you can improve the situation. The degree of charge is selected individually. Initially, traction is performed with minimum weights.
Before prescribing joint traction, an examination for possible contraindications is necessary.
popular methods
Traditional methods allow you to get rid of pain and speed up the process of restoring cartilage tissue. The following solutions can be applied:
- burdock leaves- Fresh burdock leaves are crushed until soft and applied to the affected area for 30-60 minutes. Fixation is done with gauze.
- salt compress- 50 g of salt are dissolved in 450 ml of water, after which a gauze is placed in the liquid. The gauze is removed, heated and applied to the shoulder for 45 minutes.
- Gelatin- 2 teaspoons of gelatine should be diluted in 100 ml of warm water, after which the liquid is heated to a boil. Gelatin is given orally once a day before meals. Promotes restoration of cartilage tissue.
Traditional methods will help to get a good result in therapy. It is advisable to use them during remission.
arthrosis diet
In any type of arthrosis (shoulder, wrist, ankle), it is necessary to supply the body with all the nutrients for the rapid restoration of cartilage tissue. You will need to add the following foods to your diet:
- nuts;
- Bran;
- gelatinous gelatine;
- buckwheat porridge;
- eggs.
Nutrition must be balanced. Vitamin supplements can be taken to obtain essential vitamins and minerals. It is advisable to eat 4-5 times a day. During the treatment of arthrosis, alcoholic beverages and sweets are excluded. If a person wants to achieve lasting remission, he will need to adhere to the principles of proper nutrition on an ongoing basis.
Complications and Prognosis
The prognosis depends on the person's age, the degree of damage, the individual characteristics of the organism. At a young age, it is possible to achieve complete restoration of cartilage tissue and joint functionality. In old age, you will need to adhere to certain rules to achieve lasting improvement in the condition. Arthrosis of the shoulder responds better to therapy than arthrosis of the foot, as the shoulder girdle is easy to insulate from stress. This allows for more effective conservative treatment.
Differences between arthrosis of the shoulder and arthritis
Arthrosis and arthritis have the same manifestations, but differ in clinical presentation. The main difference is that osteoarthritis is a non-inflammatory disease.In the early stages, the pain in arthrosis worries the person only after exercise and in arthritis it is constant.Arthritis is a degenerative inflammatory disease. Its treatment is a little different from that of osteoarthritis.
In order not to confuse these diseases, differential diagnosis methods are used. Laboratory and instrumental studies will help to accurately determine the presence or absence of inflammation.
Prophylaxis
The prevention of arthrosis is to eliminate the triggering factors and maintain a healthy lifestyle. You will need to do the following:
- give moderate physical activity;
- avoid hypothermia;
- use chondroprotectors;
- avoid hard physical work;
- reduce body weight to normal.
Preventive actions will help keep your joints healthy into old age. Prevention must be monitored with special care by people over 45 years of age or actively involved in sports.
conclusions
- Arthrosis of the shoulder is a degenerative disease in which there is a gradual destruction of the cartilage tissue in the joint.As a result, the person experiences pain and movement is limited.
- Treatment for the disease includesthe use of medications, the performance of physiotherapy and the performance of exercises in the physiotherapy exercise complex.
- At an early stage in the course of the disease, the prognosis for complete recovery is favorable.
- Prevention can significantly reduce the likelihood of arthrosis of the shoulder joint.

























